Using AI for Pre-Award Coordination and Grant Management
How Teams Keep Work Moving Before Submission
For cities and counties, many grant challenges surface after research and drafting are already underway.
Multiple departments are involved. Tasks depend on one another. Deadlines overlap. Supporting documents come from different teams with different priorities. Even strong applications can struggle when coordination breaks down.
Pre-award grant management is often informal. Spreadsheets, shared drives, email threads, and calendar reminders fill the gaps. As workloads increase and timelines tighten, this approach becomes harder to sustain.
As more local governments use AI across the pre-award phase, teams are beginning to apply it not just to content, but to coordination itself.
How Local Governments Coordinate Pre-Award Work Today
Most cities and counties rely on tools they already use internally.
Grant teams track deadlines in spreadsheets or calendars. Task lists live in email threads or generic project management tools. Departments are asked for inputs through meetings, follow-ups, and reminders.
A typical coordination workflow looks like this:
- Track deadlines and milestones manually
- Share requirements and drafts by email
- Follow up repeatedly with departments for inputs
- Assemble attachments close to the deadline
General-purpose AI tools sometimes help at the margins. Teams may use them to draft reminder emails, summarize meeting notes, or rephrase instructions for departments. These uses save time, but they do not change how work is organized.
Most coordination still depends on staff remembering what needs to happen next and who is responsible.
Where Coordination Becomes a Risk
As applications move closer to submission, coordination risk increases.
Tasks overlap. Departments submit inputs late or in the wrong format. Required attachments are discovered late. Changes to one section ripple across others.
General-purpose tools do not have visibility into the grant itself. They cannot see which sections are required, how tasks relate to deadlines, or which inputs are still outstanding. Staff must maintain that mental model themselves.
This is where issues often surface:
- Missed or incomplete attachments
- Sections that lag behind schedule
- Misalignment between drafts and supporting materials
- Late discovery of compliance requirements
These problems are rarely about effort. They stem from complexity and limited visibility.
Keeping Pre-Award Work Structured and On Schedule
Grant-native platforms approach coordination by treating pre-award work as a system tied directly to the grant.
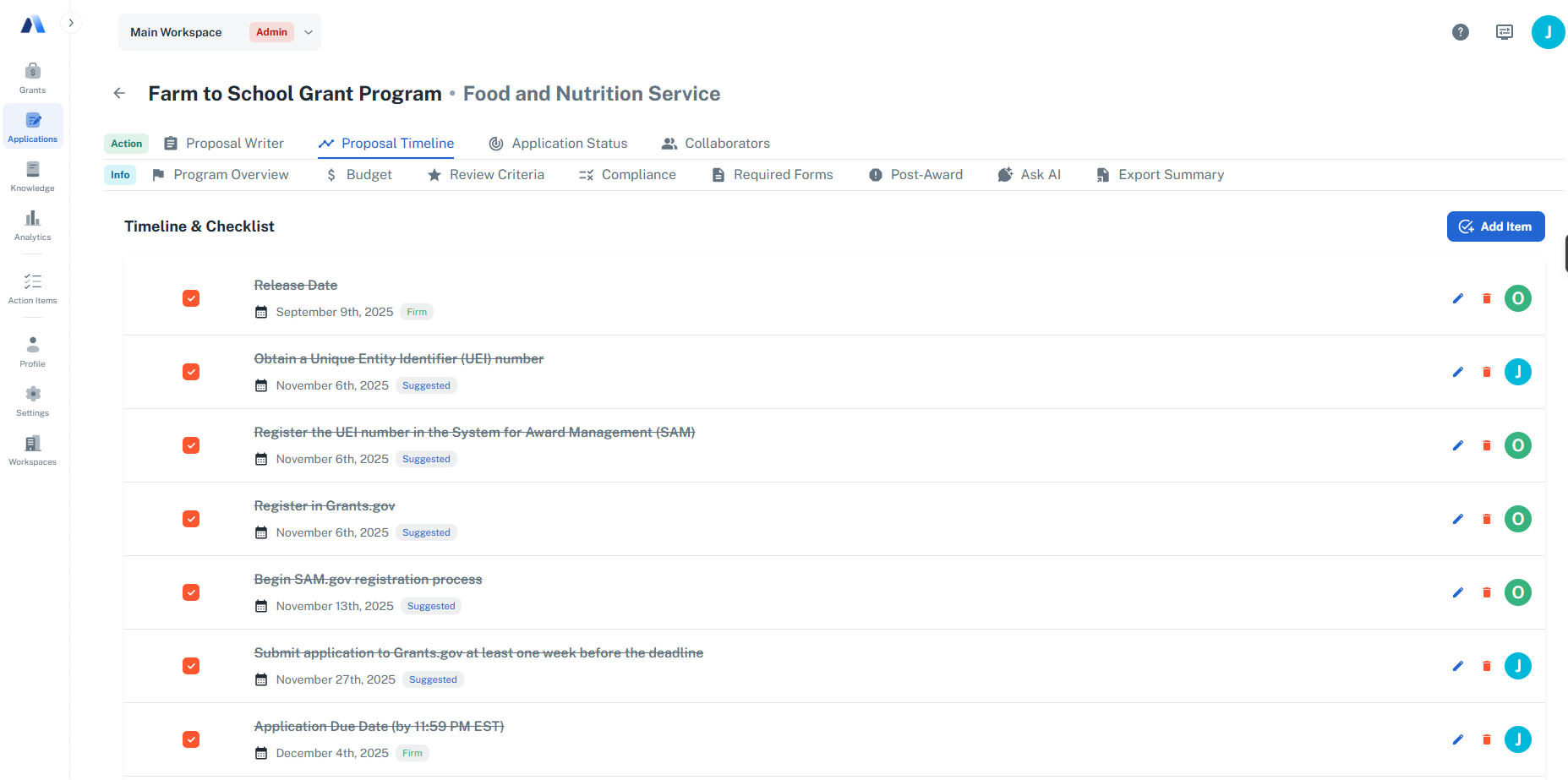
Instead of managing tasks separately from the application, timelines, assignments, and requirements live together. Work is organized around what the grant actually requires, not around reminders layered on top.
In Avila, teams use a shared timeline to:
- Assign tasks to specific collaborators
- Set deadlines tied to grant milestones
- Track progress as sections and attachments are completed
As tasks are marked complete, teams can see how close an application is to being submission-ready without manually reconciling updates across tools.
Coordinating Across Multiple Grants at Once
Most grant teams are not working on a single application.
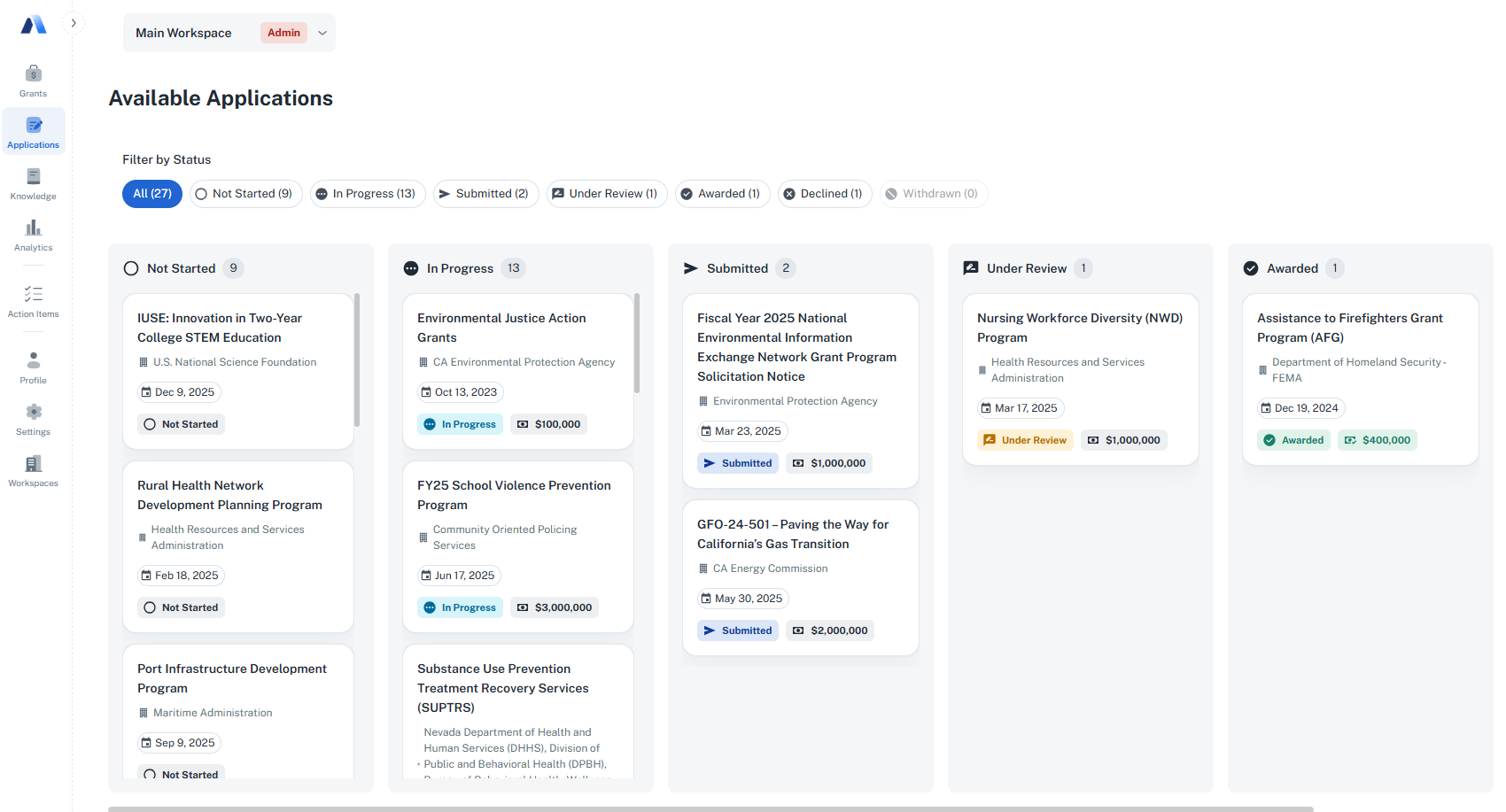
They are managing multiple opportunities at different stages, with different departments involved and different levels of effort required. Visibility across the full pipeline is often limited.
Avila pairs task-level coordination with a grant dashboard that shows progress across all active opportunities.
Teams can see:
- Which applications are not started, in progress, submitted, or under review
- Total pipeline value across current grants
- Awards received, pending decisions, and declines
- Success and completion rates over time
This makes it easier to prioritize effort, allocate staff time, and understand where applications tend to stall.
Reducing Last-Minute Scramble
As deadlines approach, coordination pressure usually increases.
With manual systems, staff are double-checking attachments, confirming page limits, and chasing last inputs. Small issues can create outsized stress.
When timelines, tasks, and application status are visible in one place, fewer surprises surface at the last minute. Teams know what remains, who owns it, and whether it aligns with requirements.
AI does not eliminate coordination work, but it reduces the cognitive load required to manage it.
Reducing Risk Without Adding Overhead
For cities and counties, better pre-award coordination is not about adding process.
It is about reducing risk.
General-purpose tools help with individual tasks. Grant-native platforms help ensure those tasks add up to a complete, compliant submission and that teams can manage multiple grants without losing visibility.
When timelines, assignments, and performance data are connected, teams spend less time managing logistics and more time strengthening applications as deadlines approach.
Summary: AI Across the Pre-Award Grant Lifecycle
Across the pre-award grant lifecycle, AI is most effective when it supports how local teams actually work, from discovery and eligibility through research, drafting, coordination, and submission readiness.
Avila brings these stages together in one system, helping cities and counties manage complexity, reduce rework, and stay aligned as applications move forward.
You can book a demo to get a walkthrough of how our tool can help you streamline this process to bring additional funding into your community.